The concept of shared cloud environments has been largely popularized in recent times. Shared cloud environments allow multiple companies to access the same infrastructure and resources. These environments are mainly aimed at improving scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility, making them a popular choice for businesses of all sizes. However, shared cloud environments may also introduce various security challenges to your workplace. As multiple entities are co-located in the same infrastructure, there are increased chances of data exposure and security breaches.
To address these challenges, companies often turn to zero-trust architecture. Zero Trust is a security model consisting of a set of principles. These principles require all users to be authenticated, authorized, and validated before they are offered access to any data or network. It also advocates access control based on the “never trust, always verify” approach. Because of the result-oriented approach of this strategy, the global zero-trust security market is expected to reach $67.9 billion by 2028. This has the potential to revolutionize the security aspects of shared cloud environments.
In this blog, we will walk you through the various principles of Zero Trust architecture in shared cloud environments. We will also familiarize you with how you can implement Zero Trust in a shared cloud.
Take the first step towards enhancing your organization’s efficiency and cost-effectiveness by implementing shared cloud services. Our expert team will help you assess your current infrastructure and tailor a shared cloud solution that meets your unique needs.
The core principles of Zero Trust:
Here is a list of some of the core principles of zero trust:

Continuous verification:Zero Trust allows organizations to continuously authenticate and authorize all the users and devices on the network based on the available data points, including location, device health, user identity, service, workload, data classification, etc. This ensures that all the devices are completely secure. Identity verification also serves as the cornerstone of security. It dictates that organizations should not automatically trust any system or user, whether inside or outside the network.
Least privilege access: This principle dictates that systems and users should always be offered the minimum permission or access required to perform a particular operation. This means limiting access to only what is necessary, reducing the chances of any users acquiring unauthorized access, and drastically reducing the risk of security threats.
Micro-segmentation: Micro-segmentation is a network security strategy that divides a network into smaller, isolated zones. Each segment has its own access controls, enhancing security by limiting unauthorized access and containing potential threats. This approach restricts lateral movement, ensuring that if one segment is compromised, the threat doesn’t easily spread to others.
Visibility and control: Companies can acquire complete visibility over all their services by opting for zero trust authentication. They also understand the number of privileged accounts associated with each service. They can control the devices allowed to connect to a particular service. Network Access Control (NAC) also regulates connections from devices in various zero trust setups.
Assume breach: The basic practice of zero trust is to assume that the network you are accessing is relatively hostile. This principle points to the fact that external and internal threats are always present in the network until and unless every single threat is ruled out. This will help ensure that the necessary steps are taken to remediate the vulnerabilities in the network.
Improve teamwork, data accessibility, and innovation within your organization. With our shared cloud services, your teams can collaborate seamlessly, securely access files from anywhere, and ensure real-time updates.
Implementing Zero Trust in shared clouds:
Implementing a secure zero trust strategy for your shared cloud environment requires several steps. Here’s a quick glance at what those steps are:
Identifying the assets: First, defining the cloud assets and data in the environment becomes necessary. This involves identifying the cloud resources, like databases, servers, storage, applications, etc., and classifying them based on various factors. It is also important to analyze the sensitivity of the data and apply encryption and backup policies accordingly.
Segmenting the network:Segmenting and isolating the cloud network forms an important part of the zero trust implementation process. It isolates the cloud network into smaller segments like microservices, virtual private clouds, and services. This helps in better regulation of traffic between the different components of the network; it also limits lateral movements in case there is a breach.
Applying security policies: The next step is to define and enforce various security policies on the assets. The policies will specify who can access what, where, when, and how in a shared cloud environment. You can also use powerful Identity and Access Management (IAM) methods like Single Sign-On (SSO) and Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) to implement role-based access control on the systems.
Automating and updating the security processes: The last step would be to automate and update the various security processes in the environment, like scanning, patching, testing, and remediation. This has a critical role to play in securing the shared cloud environment. You will also be able to remain compliant with industrial rules and regulations.
Overall, implementing a zero-trust strategy for a shared cloud environment is an ongoing process. It requires regular renewal of the security policies to remain updated with the changing threats. By adopting a zero-trust policy, companies can improve the resilience of their shared cloud environment and carry out their business operations in a streamlined way.
Applying security controls and policies in a Zero Trust network:
At the center of the Zero Trust architecture lies a security enforcement policy. All the identities, devices, networks, applications, and infrastructure components of an organization need to be configured with the appropriate security policies. The policies should also be configured so that the devices remain coordinated with the overall Zero Trust strategy of the organization.
For example, device policies can be used to determine the exact criteria for healthy devices, while conditional access policies allow healthy devices to access certain networks and applications. These policies also impact empowerment, employee, and customer engagement models and reduce the chances of data breaches.
Nowadays, companies worldwide are trying to embrace a zero-trust approach to facilitate remote work over a shared cloud network and digitally transform their business operations. Zero Trust principles can be used to establish security principles while maintaining flexibility to be on par with the fast-paced world.
Many companies implement Software-Defined Perimeter (SDP) solutions as a part of their Zero Trust strategy to dynamically create secure, micro-segmented connections for users and devices, reducing the chances of security threats. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) can also strengthen the boundaries of shared cloud environments.
The importance of monitoring and auditing in the successful implementation of Zero Trusts:
Monitoring and auditing the various cloud activities and behaviors is a vital step towards maintaining the security of the shared cloud environment. This step involves collecting and analyzing the various logs and metrics to improve the visibility of the different operations of the cloud environment.
Through rigorous governance, the cloud activities offers insight into the performance of the various assets. Utilizing highly advanced monitoring tools like User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA) can be used to detect any suspicious activities or anomalies in the cloud environment.
Continuously monitoring the security boundaries of an organization using Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions can also help identify vulnerabilities, outdated software, or signs of compromise on devices.
Securing the Future with Indium Software’s Zero Trust Solutions:
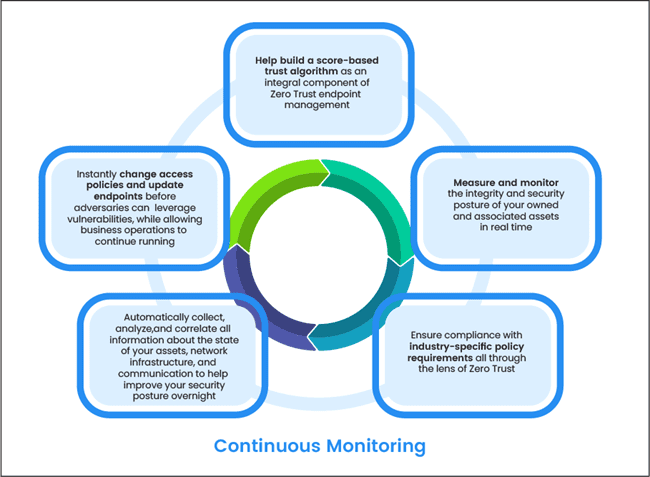
Now, you can streamline your Zero Trust journey amid all your business operations with Indium Software. By choosing Indium Software as your Zero Trust implementation partner, you can ensure that all your assets and endpoints meet the NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) requirements. The experts at Indium Software will help you deploy tools and techniques to manage the security aspects of your shared cloud environment dynamically.
You can instantly change and monitor access policies while allowing your business operations to run smoothly. Zero Trust also provides you the scope to collect, analyze, and correlate information about the state of the different assets in your environment in real time. So, if you are willing to revamp your security strategy, contact the experts at Indium Software and avail of their services.
Protect your sensitive data and streamline data management with our shared cloud services. Our cutting-edge security measures and robust data sharing capabilities ensure your information is safe and accessible only to authorized users.
Conclusion:
As companies have increased their reliance on shared cloud setups, it has become imperative for organizations to implement a zero-trust strategy in their workplace environment. The “never trust, always verify” approach, coupled with robust identity and access management, network segmentation, security control, and continuous monitoring, provides a strong foundation for securing shared cloud services. By implementing Zero Trust, you will be able to safeguard your critical assets and manage the boundaries of your shared cloud environment much better.





